

Ongkudon CM, Danquah MK (2010) Process optimisation for anion exchange monolithic chromatography of 4.2 kbp plasmid vaccine (pcDNA3F). Matos T, Queiroz JA, Bülow L (2013) Binding and elution behavior of small deoxyribonucleic acid fragments on a strong anion-exchanger multimodal chromatography resin. Yamamoto S, Nakamura M, Tarmann C, Jungbauer A (2007) Retention studies of DNA on anion-exchange monolith chromatography Binding site and elution behavior. Yamamoto S, Yoshimoto N, Tarmann C, Jungbauer A (2009) Binding site and elution behavior of DNA and other large biomolecules in monolithic anion-exchange chromatography. Ghanem A, Healey R, Adly FG (2013) Current trends in separation of plasmid DNA vaccines: a review. Liu MA (2011) DNA vaccines: an historical perspective and view to the future. Pereira LR, Prazeres DMF, Mateus M (2010) Hydrophobic interaction membrane chromatography for plasmid DNA purification: design and optimization. Sousa A, Sousa F, Queiroz JA (2012) Advances in chromatographic supports for pharmaceutical-grade plasmid DNA purification. This behaviour can be linked to the presence of the more hydrophobic phenyl group in Capto Adhere, leading to stronger retention of ssDNA molecules, which have a more hydrophobic character due to a higher degree of base exposure. Another pronounced difference between the resins was observed in the inverted elution of ss- and dsDNA, where ssDNA eluted at 2.88 M NaCl on Capto Adhere, while on Capto Q ImpRes ssDNA eluted already at 1.47 M NaCl. This recognition was not observed for Capto Adhere. Capto Q ImpRes provided a recognition for guanylate bases when samples of deoxynucleotides or poly(dG) were examined. All deoxynucleotides and DNAs tested bound strongly to the chromatographic materials and could be eluted by a linear gradient of increasing NaCl concentration.
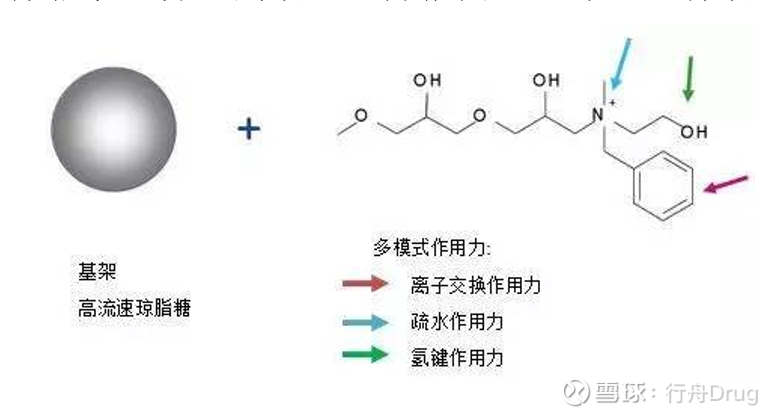
These variations in biophysical properties have been utilized for comparative separations on these two resins. The intrinsic differences between single- and double-stranded DNAs are related to charge, hydrophobicity, size and three-dimensional structure. Capto Adhere carries a multimodal ligand which combines strong anion with aromatic recognition, while Capto Q ImpRes is a strong anion exchanger with a chemically similar ligand, but without a phenyl group. When working with sensitive MAbs, the wide window of operation simplifies optimization of conditions.The differences in chromatographic behaviour of individual deoxynucleotides as well as small single-stranded and double-stranded DNA molecules have been examined for two resins from the Capto family: Capto Adhere and Capto Q ImpRes. The wide window of operation for conductivity and/or pH simplifies the process as conditioning after the protein A step can be omitted. Suitable for sensitive MAbs and other biomoleculesĬapto MMC ImpRes can be used for initial or final polishing steps in MAb purification processes, as well as for the polishing of antibody fragments such as domain antibodies (DAbs). The multimodal cation exchanger ligand of Capto MMC ImpRes is immobilized to the base matrix and interacts with the target molecule through multiple types of interactions. The weak cation exchange multimodal ligand enables high selectivity in a broad pH/salt window compared with traditional ion exchangers, which allows the use of Capto MMC ImpRes in a variety of process conditions to solve challenging purification problems. Suitable for polishing of antibody fragments.Displays a broad pH/salt operational window.Enables use of a platform approach to MAb process development.Efficient removal of aggregates, viruses, and main contaminants in MAb processes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
